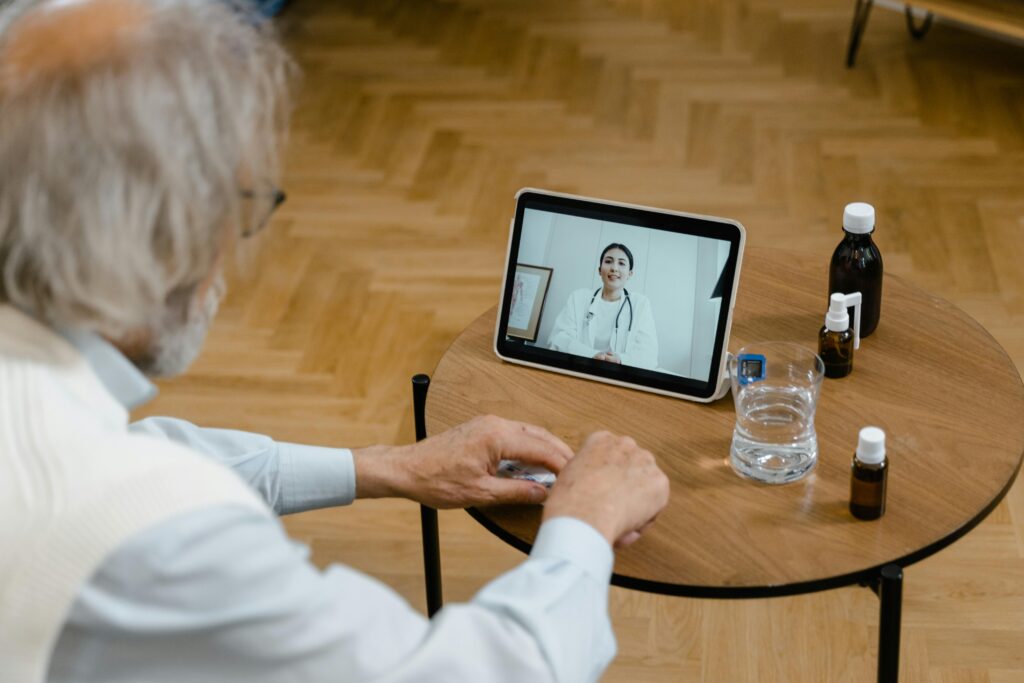
Chronic diseases affect millions worldwide, placing a significant burden on healthcare systems. The World Health Organization reports that chronic diseases account for 74% of all deaths globally. One of the most promising methods of chronic disease management is remote patient monitoring (RPM). Let’s explore how RPM helps people with chronic disease have a better quality of life.
Contents
What is Remote Patient Monitoring?
RPM is a healthcare delivery method that uses technology to collect patient data outside of traditional healthcare settings. But what exactly does this mean for patients and healthcare providers?
Definition of remote patient monitoring
RPM involves using digital technologies to gather and transmit health data from patients to healthcare providers. This allows for continuous monitoring of a patient’s health status without the need for frequent in-person visits.
Key components of RPM systems

A typical RPM system consists of several essential components:
- Sensing devices: These collect patient data such as blood pressure, heart rate, or blood glucose levels.
- Data transmission: The collected data is sent securely to healthcare providers.
- Data analysis: Healthcare professionals review and interpret the data.
- Patient interface: Patients can view their data and receive feedback through apps or web portals.
- Alert systems: Automated alerts notify healthcare providers of any concerning changes in a patient’s condition (Peyroteo et al., 2021).
Types of data collected through RPM
RPM systems can collect various kinds of health data, including:
- Vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure, temperature)
- Blood glucose levels
- Weight
- Oxygen saturation
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) readings
- Activity levels and sleep patterns
This comprehensive data collection allows healthcare providers to gain a more complete picture of a patient’s health over time.
Common Chronic Diseases Managed with RPM
RPM is effective in managing many kinds of chronic conditions. Let’s look at some of the most common diseases that benefit from RPM.
Heart disease, CHF, and hypertension
RPM plays a crucial role in cardiovascular disease management, including heart disease, chronic heart failure (CHF), and hypertension (Zhang, et al., 2023).
Patients can regularly monitor their blood pressure, heart rate, and other vital signs at home. This continuous monitoring helps healthcare providers to adjust medications and interventions as needed, which may prevent heart attacks and strokes.
Diabetes

For patients with diabetes, RPM can be a game-changer. Continuous glucose monitoring systems allow for real-time tracking of blood sugar levels, helping patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about insulin dosing and lifestyle changes. Studies have shown that RPM can lead to significant improvements in HbA1c levels, a key indicator of long-term blood sugar control.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD)

RPM is becoming increasingly important in kidney care by using technology to support patients who need renal replacement therapy (RRT).
RPM can improve patient outcomes, reduce hospital stays, and enhance treatment adherence. It also saves time and money for both patients and healthcare providers. A care plan for chronic kidney disease that includes RPM can help with patient education, CKD self-management, and home dialysis care. They can increase patient independence and improve their quality of life (Mata-Lima, 2024).
Asthma

For asthma patients, RPM can help track symptoms, medication use, and lung function. This information allows healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans and identify triggers, leading to better asthma control. A review of RPM interventions for asthma found improvements in quality of life and reductions in emergency department visits.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)

COPD patients can benefit greatly from RPM. When health providers monitor oxygen levels, lung function, and symptoms, they can detect exacerbations early and intervene before hospitalization becomes necessary.
Anemia
Anemia, a condition characterized by a deficiency of red blood cells or hemoglobin, affects millions worldwide. It can lead to fatigue, weakness, and other health complications. RPM can helps manage anemia in many ways:
- Continuous Monitoring: RPM devices can track hemoglobin levels and other vital signs and anemia symptoms remotely. This is particularly beneficial for patients in remote areas where access to healthcare facilities is limited.
- Early Detection: RPM can help detect anemia-related complications early by collecting data on patients’ blood oxygen levels and other indicators. This allows for timely interventions, reducing the risk of severe health issues.
Now let’s look at specific benefits of using RPM to manage chronic conditions.
Benefits of RPM for Chronic Disease Management
Implementing RPM in chronic disease management has several advantages for both patients and healthcare systems.
Early detection of health issues
One of the most significant advantages of RPM is its ability to detect potential health issues early. By continuously monitoring patient data, healthcare providers can identify concerning trends or sudden changes before they become serious problems. This proactive approach can lead to timely interventions and prevent complications (Peyroteo et al., 2021).
Improved medication adherence
Medication adherence is crucial for managing chronic diseases effectively. RPM systems often include medication reminders and tracking features, which can significantly improve adherence rates. A review of multiple studies found that RPM interventions increased medication adherence by an average of 22%.
Better patient engagement and self-management

RPM empowers patients to take an active role in managing their health. A real-world use study reported RPM helps better adherence to CHF treatment regimens (Patrick et al., 2023). And RPM adherence is associated with better patient outcomes (Sabatier et al., 2022).
By providing real-time feedback and educational resources, these systems help patients better understand their conditions and make informed decisions about their care. This increased engagement can lead to improved health outcomes and quality of life for those living with chronic diseases (Peyroteo et al., 2021).
Reduced hospital readmissions

RPM has shown promising results in reducing hospital readmissions for patients with chronic conditions.
A study published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research found that RPM reduced 30-day hospital readmissions by 76% for patients with heart failure (Bashi et al., 2017). And another study showed a reduction in hospitalizations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients using RPM (Polsky et al., 2023).
Fewer trips back to the hospital improves patient outcomes and helps reduce healthcare costs.
Cost savings and effectiveness
Noninvasive RPM can be cost-effective compared to traditional methods for managing chronic disease (De Guzman et al., 2022).
RPM requires an initial investment in equipment and training. But over the long run, it can reduce healthcare costs long-term by preventing expensive health events like hospital readmissions, although those savings may take time to manifest. Technology advances may lower costs over time.
The level of cost-effectiveness also varies by disease and context. Studies on hypertension, COPD, and heart failure show the highest benefits for hypertension. Effectiveness depends on patient targeting and integration into existing healthcare systems. Local factors and clinical settings influence RPM’s cost-effectiveness, which emphasizes the need for tailored implementation plans.
RPM Technologies and Devices
The success of remote patient monitoring relies heavily on the technologies and devices used to collect and transmit patient data. Let’s explore some of the key tools in the RPM arsenal.
Wearable devices and sensors

Wearable technology has come a long way in recent years. These devices can now track a wide range of health metrics, including:
- Heart rate and ECG
- Blood pressure
- Physical activity and sleep patterns
- Blood oxygen levels
Many of these devices are designed to be comfortable and discreet, allowing for continuous monitoring without disrupting daily life.
Mobile health apps
Mobile health apps serve as the interface between patients and their health data. These apps often provide:
- Data visualization and trends
- Medication reminders
- Educational resources
- Communication tools for connecting with healthcare providers
The user-friendly nature of these apps makes it easier for patients to stay engaged with their health management.
Home-based monitoring equipment

For more specialized monitoring, home-based equipment can provide detailed health information. This may include:
- Blood glucose meters
- Spirometers for lung function testing
- Digital scales for weight monitoring
- Blood pressure cuffs
These devices are designed to be easy to use, allowing patients to take accurate measurements at home.
Data transmission and analysis platforms
The backbone of any RPM system is the platform that receives, stores, and analyzes patient data. These platforms use secure cloud-based systems to:
- Aggregate data from multiple sources
- Apply algorithms to detect patterns and anomalies
- Generate alerts for healthcare providers
- Provide detailed reports for clinical decision-making
How to Implement RPM in a Healthcare Setting
While the benefits of RPM are clear, implementing these systems in healthcare settings can be challenging. Here are some key considerations for successful RPM implementation.
Choose the right RPM solution
Selecting an appropriate RPM solution is crucial for success. Healthcare providers should consider:
- The specific needs of their patient population
- Integration capabilities with existing electronic health record systems
- User-friendliness for both patients and healthcare staff
- Scalability to accommodate future growth
It’s important to evaluate multiple options and pilot test solutions before full implementation.
Train healthcare providers and patients

Proper training is essential for both healthcare providers and patients to ensure effective use of RPM systems. This may include:
- Hands-on training sessions for healthcare staff
- Patient education materials and support resources
- Ongoing technical support for troubleshooting issues
Investing in comprehensive training can significantly improve adoption rates and overall success of RPM programs.
Integrate RPM with existing health IT systems
Seamless integration with existing health information technology systems is crucial for success with RPM, which allows for:
- Automatic data transfer to electronic health records (EHRs)
- Streamlined workflow for healthcare providers
- Comprehensive patient health profiles
A smooth integration takes a collaborative effort between IT teams, RPM vendors, and healthcare staff.
Address privacy and security concerns
As with any system handling sensitive health information, privacy and security are paramount in RPM. Healthcare organizations must:
- Implement robust data encryption measures
- Ensure compliance with HIPAA and other relevant regulations
- Regularly audit and update security protocols
- Educate patients on best practices for protecting their health data
Overcoming Challenges in RPM Adoption
While RPM offers numerous benefits, there are several challenges that healthcare organizations must address for successful adoption.

Reimbursement and insurance coverage
One of the primary barriers to RPM adoption has been uncertainty around reimbursement. However, recent changes in healthcare policies have improved the situation:
- Medicare now provides reimbursement for certain RPM services
- Many private insurers are following suit because they understand the cost-saving potential of RPM
Healthcare providers should stay informed about evolving reimbursement policies and advocate for expanded coverage.
Patient compliance and technology acceptance

For RPM to be effective, patients must consistently use the provided monitoring devices and follow recommended protocols. Strategies to improve compliance include:
- Selecting user-friendly devices and apps
- Providing ongoing patient education and support
- Using motivational techniques, such as gamification or reward programs
- Tailoring RPM programs to individual patient needs and preferences
Data management and interpretation
The large volume of data generated by RPM systems can be overwhelming for healthcare providers. To address this challenge:
- Implement robust data analytics tools to identify meaningful trends and anomalies
- Provide training for healthcare staff on data interpretation
- Develop clear protocols for responding to alerts and abnormal readings
- Consider incorporating artificial intelligence to assist with data analysis
Regulatory and legal considerations
As RPM technology evolves, regulatory frameworks are struggling to keep pace. Healthcare organizations must navigate:
- Evolving FDA regulations for medical devices and software
- State-specific telemedicine laws and licensing requirements
- International considerations for cross-border remote care
Staying informed about regulatory changes and working with legal experts can help organizations navigate these complex issues.
The Future of RPM in Chronic Disease Management
As technology continues to advance, the future of RPM in chronic disease management looks promising. Here are some exciting developments on the horizon.

Artificial intelligence and machine learning integration
AI and machine learning take RPM to the next level as they can:
- Improve predictive analytics for early intervention
- Personalize treatment recommendations based on individual patient data
- Automating routine tasks to free up healthcare provider time
- Enhancing pattern recognition for more accurate diagnoses
Expansion of RPM to new disease areas
While RPM has proven effective for common chronic conditions, we’re likely to see its application expand to other areas, such as:
- Mental health monitoring
- Neurological conditions like Parkinson’s disease
- Post-surgical recovery and rehabilitation
- Rare diseases that require specialized monitoring
Potential for population health management

RPM data, when aggregated and analyzed at a population level, can provide valuable insights for public health initiatives. This could lead to:
- More targeted health interventions
- Improved resource allocation in healthcare systems
- Better understanding of disease trends and risk factors
- Enhanced ability to respond to public health crises
Evolving healthcare policies and regulations
As RPM becomes more widespread, we can expect to see:
- Continued expansion of reimbursement policies
- Development of standardized guidelines for RPM implementation
- Increased focus on interoperability standards for health data exchange
- Greater emphasis on patient data ownership and privacy rights
RPM offers a proactive approach to chronic disease management that benefits both patients and providers. By enabling continuous, real-time health tracking and timely interventions, RPM can significantly improve patient outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and enhance the quality of life for those living with chronic conditions.
As technology continues to advance and healthcare systems adapt, the role of RPM in chronic disease management will likely expand, paving the way for more personalized and efficient healthcare delivery. Embracing this innovative approach can lead to a healthier future for millions of people worldwide.
References
Bashi, N., Karunanithi, M., Fatehi, F., Ding, H., & Walters, D. (2017). Remote Monitoring of Patients With Heart Failure: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. Journal of Medical Internet Research; 19(1). doi.org/10.2196/jmir.6571
Centellas-Pérez, F. J., Ortega-Cerrato, A., et al. (2023). Impact of Remote Monitoring on Standardized Outcomes in Nephrology-Peritoneal Dialysis. Clinical Research; 9(2),266-276. doi.org/10.1016/j.ekir.2023.10.034
De Guzman, K. R., Snoswell, C. L., Taylor, M. L., Gray, L. C., & Caffery, L. J. (2022). Economic Evaluations of Remote Patient Monitoring for Chronic Disease: A Systematic Review. Value in Health; 25(6), 897-913. doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2021.12.001
Fakunle, A. (2022). The Future of Healthcare: How Remote Patient Monitoring Transforms Healthcare. Cleverdev Software. Retrieved from https://www.cleverdevsoftware.com/blog/the-future-of-healthcare
Mata-Lima, A., Paquete, A. R., & Serrano-Olmedo, J. J. (2024). Remote patient monitoring and management in nephrology: A systematic review. Nefrología. doi.org/10.1016/j.nefro.2024.01.005
Noncommunicable diseases. (2023). World Health Orgination (WHO). Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases
Patrick, J., Picard, F., Girerd, N., et al. (2023). Security and performance of remote patient monitoring for chronic heart failure with Satelia® Cardio: first results from real-world use. Journal of Cardiology and Cardiovascular Medicine; 8:042–50. doi:10.29328/journal.jccm.1001152
Peyroteo, M., Ferreira, I. A., Elvas, L. B., Ferreira, J. C., & Lapão, L. V. (2021). Remote Monitoring Systems for Patients With Chronic Diseases in Primary Health Care: Systematic Review. JMIR MHealth and UHealth; 9(12). doi.org/10.2196/28285
Polsky, M., Moraveji, N., Hendricks, A., Teresi, R. K., Murray, R., & Maselli D. J. (2023). Use of Remote Cardiorespiratory Monitoring is Associated with a Reduction in Hospitalizations for Subjects with COPD. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease; 18:219-229. doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S388049
Sabatier, R., Legallois, D., Jodar, M., et al. (2022). Impact of patient engagement in a French telemonitoring programme for heart failure on hospitalization and mortality. ESC Heart Failure; 9(5):2886–2898. doi:10.1002/ehf2.13978
Telehealth Interventions to Improve Chronic Disease. (2024). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/cardiovascular-resources/php/data-research/telehealth.html
Zhang, Y., Peña, M. T., Fletcher, L. M., Lal, L., Swint, J. M., & Reneker, J. C. (2023). Economic evaluation and costs of remote patient monitoring for cardiovascular disease in the United States: a systematic review. International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care;39(1):e25. doi:10.1017/S0266462323000156