The intersection of chronic illness management and in-home caregiving presents unique challenges in healthcare. Through a compelling blend of personal storytelling and empirical data, this article illuminates the often-overlooked daily struggles of working caregivers.
I examine how emerging technologies and care models, such as remote patient monitoring and care-at-home programs, can transform the caregiving experience, offering valuable perspectives for healthcare providers and health plans seeking to integrate effective care solutions.
—
Contents
- The Downward Spiral
- Effects of In-Home Caregiving by Working Adults
- Navigating Healthcare Systems and Insurance Complexities
- Supporting Caregivers and Their Families
I married a man just two months after we met, because if I didn’t, I knew he was going to die.
I met George on a dating site in March 2016 as “PuertoRicanPapi.” During our first phone conversation, I learned he had been diagnosed with Stage 4 end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and only had 18 months to live. He needed to start dialysis, but his ACA health plan wouldn’t cover it.
The Global Burden of Disease ranks chronic kidney disease (CKD) among the top 20 causes of death (Ibrahim et al., 2022). CKD is regarded as a high-stress illness due to the chronicity of the disease and the long-term treatment required. ESRD is the last stage of CKD, often caused by diabetes mellitus.
That’s a heavy thing to hear from anyone. But there was something about him that wouldn’t let me leave him alone.
The Downward Spiral
The Diabetes Domino Effect
George was a 40-year-old Puerto Rican man with diabetes, neuropathy, and ESRD. The following year, he developed non-Hodgkins lymphoma (NHL) and eventually sepsis. Over the course of our 2 years together, I coordinated his care among 10 doctors (primary care and various specialists).
His diabetes diagnosis is unclear, as some of his doctors mentioned Type 1 and others said it was Type 2. But from what I understand, before we met, a clinic had prescribed him insulin pills when he actually needed the insulin pens.

That’s a heavy thing to hear from anyone. But there was something about him that wouldn’t let me leave him alone.
Peritoneal Dialysis and the Hospital Revolving Door
That fall, George got surgery to implant a port into his belly, and then we started peritoneal dialysis (PD) from home. I set up the machine and ran it for him every night as I was taught by his nephrology team. But every month he went to the hospital because:
- A1C was high,
- His hemoglobin count was low (especially after chemotherapy) and he needed a blood transfusion, or
- He was in pain.
He didn’t like being there because no one would let him rest, nutritionists came in to tell him how to eat properly for a diabetic and renal diet (and often those menus were contradictory), and other clinicians would come in and ask the same questions every time. I occasionally stayed overnight with him if my daughter was accounted for.

Weekends were the worst, because when he was having intense pain, he had to visit the ER for relief, of course waiting all day for his name to be called.
We also enrolled in a kidney transplant program at Emory Hospital in Atlanta, GA. Although I wasn’t a match to be a kidney donor for George, I was eligible to be in an exchange program with someone else, and they could provide a matching kidney for George. Unfortunately, the next setback negated these efforts.
Developing Cancer

George saw the dentist for pain in his mouth a few times in the fall of 2016 and spring of 2017. The dentist found an abnormality in his mouth that kept coming back.
During that last visit, George went to the hospital, they tested it and it was cancer–Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma (NHL).
He started chemotherapy later that month. His beautiful hair started shedding on the pillowcase the next day, and mourning began.
Losing his Leg
A few months later, George fell in our bathroom upstairs while I was in New York at my grandmother’s funeral. His teenage daughter was home, but downstairs. She called me two days later to tell me that he fell, and that his foot was black.
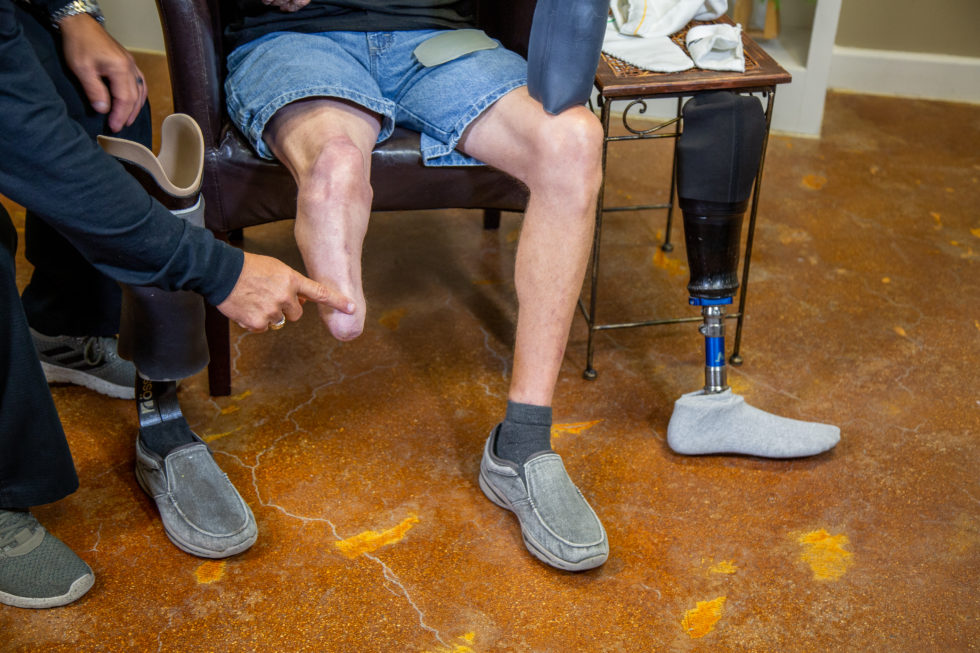
Type 2 diabetes often causes complications that can lead to lower limb amputation (Costa et al., 2020), and unfortunately, this is when George’s health took a turn for the worse. We went to a specialist after I got back from New York, who confirmed his left foot was broken and would probably never heal correctly, and recommended a below-the-knee amputation. George was devastated, but went through with it.
Afterward, he could still drive with his right foot, and he decided to buy a large SUV. I assisted him with getting in and out of the truck with his new wheelchair. However, we no longer slept together, because our bedroom was upstairs. He stayed on the couch for a few months until we got a hospital bed placed in the living room.
Losing Hope
Even though he was taking several prescribed high-dose narcotics, they didn’t have much effect in pill or patch form. Only medicines administered by IV quelled his suffering.

I always felt like I had to be strong, but I was at my wits end, suffering silently beside him. The last straw was when he developed gangrene on his genitalia, and it wasn’t curable. His pain intensified, and I advocated for him tirelessly by calling doctors, and researching information, but it was impossible to get pain management from any doctor in our city, so he suffered needlessly.
Multiple calls to his nephrologist and primary care doctor were never addressed, so I believed that palliative care was the only thing that would make him comfortable. In January 2018, I admitted him to hospice care, where he died a couple months later. I didn’t receive follow-up counseling afterward, but I met with my therapist a few more times until I moved out of state and back near my family to grieve.
Looking Back
The single most important thing missing from my experience that would have made things easier is access to support, which I describe in the following DECAF section.
I balanced parenting and school functions with spousal caregiving, administrative duties like tracking his medications, scheduling new appointments and conferring with health insurers, transporting my husband to multiple appointments, household responsibilities, and my full-time work as a technical writer with a Fortune 50 corporation. And I didn’t receive support from providers after his death, except for a newsletter from the hospice team every few months until a year passed.
I could have used an assistant for appointment scheduling and insurance coordination. A home health aide at flexible times to help with toileting and other ADL tasks.
Effects of In-Home Caregiving by Working Adults
During the pandemic, parents of school-aged children learned what it’s like to try balancing the role of teaching them while also managing their own work and household responsibilities. In-home caregiving was similar in my experience-–I had to juggle my work duties working from home with caring for my husband, and it wasn’t easy.

A study of the estimated 8.8 million employed family caregivers found that nearly 1 in 4 (23.3%) reported either absenteeism or presenteeism over a 1-month period due to caregiving (Fayete et al., 2023). Among those affected, caregiving reduced work productivity by one-third on average—or an estimated $5,600 per employee when annualized across all employed caregivers—primarily because of reduced performance while present at work. Productivity loss was higher among caregivers of older adults with significant care needs and varied according to sociodemographic characteristics and caregiver supports.
CareYaya Health Technologies’ data shows that caregivers spend an average of 15 to 20 hours per week on caregiving tasks. “It’s super hard to draw the line between when you’re working and when you’re caregiving when you’re WFH,” says CEO Neal K. Shah.
“70% of caregivers worldwide are women, and their average age is 49,” says Cheryl Field, MSN, RN. “So if you think about the multiple roles that a 49-year-old woman is playing between their own children, their career, their parents, their partner and the biological changes that come with menopause, you can see that caregivers are in a particularly pressure-filled time of their life. Any means by which they can reduce some of these stressors is significant.”
Stress from Multitasking

Caregiving influences several dimensions of the caregiver’s life, such as physical (e.g., physical health deterioration), psychological (e.g., anxiety and traumatic stress), family (e.g., roles and routines) and social (e.g., leisure time and social life) (Costa et al., 2020). Caregivers under stress report high levels of depressive symptoms, anxiety, high use of psychotropic drugs, low satisfaction with life, several symptoms related to psychological stress, and low subjective health.
“In-home caregiving lends itself to both more and less stress for the caregivers,” notes Dr. Caryn McAllister of High Quality Therapy. “Caregivers who work from home can juggle responsibilities needed during the day with work, and flexibility with respect to hours can allow people to contact medical professionals, organize schedules, and ensure their loved one eats, goes to the bathroom and takes medicines on time. The extra stress can come when people don’t have the ability to transition between work and home life. People often find they can leave work at work when they go home, but caregivers who work from home just don’t get that break. Ever! It takes organization and discipline to make it work.”
Wil Thomas, Editor of the Senior Bulletin, mentions a reader named John who echoes these sentiments. John has a full-time job while taking care of his elderly mother. “It’s like having two full-time jobs,” he says. “I’m constantly juggling meetings and her medical appointments, and it’s exhausting.”
Field understands this, too. As a former chief product officer who had a senior living with her in a multigenerational setting. She highlighted that the impact of providing in-home care varies over the course of the patient’s illness. “When care needs can be anticipated and scheduled, and additional resources can be utilized to put a plan in place, the impact can be smaller. When care needs are unexpected or difficult to anticipate, the impact will be greater,” she says.

“Consider that your interrupted sleep several times a week in the middle of the night over a chronic period of time begins to have an impact on your own rest and even the ability to fall asleep with anticipated anxiety of what’s to come through the night,” Fields continues. As care needs become more demanding on working adults, often you’ll see a rise in absenteeism for scheduled and unscheduled medical needs, and a decrease in resiliency on behalf of the employee. Chronic fatigue, fear, stress and anxiety all compound and can have an impact on the health of the working adult.”
Unfortunately, these stories aren’t unique. For adults who are caring for a loved one and also continuing to work in their career, taking on these responsibilities can be stressful and lead to burnout, Field says. 60% of caregivers are also employed, and many feel the job-related stress piling up. But working from home does make a big difference, providing flexibility that in-home caregivers need.
Impact of Diabetes on Patients and Chronic Care
50% to 75% of people with diabetes have a caregiver involved in their healthcare (Fields et al., 2022). These caregivers are often partners, spouses, adult children, or siblings.
Like many chronic conditions, diabetes requires complex medical management that often requires following regimented eating plans, monitoring sugar levels, organizing daily medications, and coordinating medical care. The sicker George became, the more of these responsibilities fell on me.

The chronic care model is a multidimensional solution to the complex problem of providing care to patients with chronic health problems. The theory of this model says that a significant part of chronic care takes place outside of formal healthcare facilities (Katsarou et al., 2023).
It also states that six elements are central to initiatives to improve chronic care: community resources, healthcare system, patient self-management, decision support, service delivery system redesign, and clinical information systems. Interventions that include at least one of these elements are associated with improved outcomes for people with asthma, diabetes, heart failure, and depression. However, only patients with heart failure and depression had improved quality of life (Katsarou et al., 2023).
Flexible scheduling

Caregiving would have been impossible if I couldn’t work from home. George had 10 doctors, and that translated to roughly 3 days a week with at least one appointment. At that point, I had worked for my company for almost 20 years, which gave me unlimited sick time and lots of vacation time. I took my work laptop with me to doctor appointments, rearranged meetings, and still made time for my daughter’s activities.
Working from home gave me flexibility in managing caregiving tasks and professional responsibilities, including the ability to respond to his needs promptly, compared to me working in an office setting, or George being in a facility where staff are spread across multiple patients.
Another of Thomas’ readers, Jane, works remotely and looks after her father, who has Alzheimer’s. “Working from home has been a lifesaver,” she says. “I can attend to my dad’s needs throughout the day without compromising my work. It’s still challenging, but having that flexibility makes a huge difference.”
While working from home offers more flexibility to manage caregiving tasks, it can also blur the lines between work and caregiving responsibilities. “Many caregivers report feeling constantly “on-call,” which can lead to burnout, and that burnout affects over 33% of family caregivers who are working from home, compared to 20% who work in the office,” Shah reports.
Indeed, flexible work arrangements such as telecommuting, job-sharing, and flexible hours can help caregivers manage their time more effectively. However, since the pandemic ended, return-to-office mandates have flourished with employers who want to manage employees in person and/or fill their empty office spaces. 90% of companies plan to implement return-to-office policies by the end of 2024, according to a report from Resume Builder. Nearly 30% say their company will threaten to fire employees who don’t comply with in-office requirements.
But for employees who can work remotely, several caregiver pressures can be relieved. Removing the commute and a strict start or end time of an office job gives the remote employee flexibility. Fields gives some of examples:
“On mornings where there’s been a difficult night, an extra hour of sleep can make a world of difference on how the employee feels and functions that day. Being able to work from home may also make it possible to leverage telehealth appointments instead of having to physically travel to doctor’s appointments. Caregivers also have the ability to provide distant supervision and mealtime support for a loved one while working from home and don’t need to have as many outside resources coming into the home to provide that supervision or ensure meals are delivered and consumed. These small benefits relieve a lot of microstress.”
Caregiver Needs Analyzed with DECAF
A study at the University of West Attica in Greece investigated the needs of caregivers of patients suffering from CKD, stroke, cancer, dementia and multiple sclerosis (Katsarou et al., 2023). 89% of these caregivers were relatives, 50% were between 20 and 50 years old, and 19% were spouses. Researchers found themes among caregiver needs:

- Caregiver training
- Help with nursing home care and physical therapy
- Help with financial burden from health services
- Lack of reliable transport
- Psychological support, including delivery via digital media and mobile devices
- Social support groups
- Navigating complex medical insurance
I agree with all of these points. To break it down a bit more, I’m using the DECAF framework (Fields et al., 2022), which was developed to raise awareness about caregiver responsibilities in care planning and execution during the hospital-to-home transition. Here’s how DECAF played out in my caregiving experience.
Direct Care Provision
Direct Care Provision refers to hands-on support with activities of daily living (ADLs) such as getting dressed, food preparation, toileting and physical activities, and taking the patient to healthcare appointments. It also includes nursing tasks like wound care and medication management. I was a certified nursing assistant in the 90s, and a home health aide in the 2000’s, both of which prepared me for my experience with George.
Emotional Support
Emotional Support is the empathy and compassion for the patient and caregiver.
I had no close friends nearby, and George’s family was local, but most of them were more hands-off. So as his condition took more and more of a toll on my mental health, I sought out family members, a therapist, and church groups for support and stress relief.
Social support can diminish the impact of the emotional burden and stress of care by providing solutions to problems, distractions from issues or facilitating the required healthy behaviors (Ibrahim et al., 2022). Caregivers who seek social support from family and friends experience a lesser burden of care than caregivers without solid support networks.

Seeking social support is the dominant coping mechanism for caregivers of patients undergoing renal replacement therapy (Ibrahim et al., 2022). Caregivers of chronic patients are four times more likely to be diagnosed with depression and three times more likely to seek help for anxiety issues than individuals who are not caregivers.
Being an in-home caregiver is lonely, and I lacked self-care. I’ve been working from home since 2005 so I was used to being alone, but caregiving for your spouse is a different kind of loneliness. I was losing my husband slowly as his condition got worse, and I needed social support. I mostly relied on my family (long-distance phone calls) and a local church group. In less than a year, I shifted from being a newlywed with an independent husband to a caregiver. My marital needs were not met, as George lost sexual function early on. This also caused strain on our relationship.
I’m not alone. A study on psychological health from Savitribai Phule Pune University in India confirms that dysfunctions caused by chronic illnesses aren’t limited to the patient, but affect the partner, and the couple’s dynamic, making a considerable impact on the satisfaction levels in the relationship (Umrigar and Mhaske, 2022). Behavioral and personality changes in the patient can overpower emotional bonds between the caregiver and the patient as well. The greater the negative effect, the greater the frequency of depression, anxiety, and somatization in the caregiver.

This study polled women caregivers about their male spouses with chronic conditions of cancer, coronary heart disease, and diabetes. They found clinically significant marital and sexual dissatisfaction. Since marital satisfaction and sexual satisfaction are closely linked, a decrease in one tends to have a serious impact on the other, and consequently, on the overall quality of life.
Care Coordination
Care Coordination involves initiating, managing and maintaining healthcare services and support. Managing diabetes successfully requires significant care organization and coordination of multiple types of interactions with the healthcare system. Participants in a study at the University of Wisconsin-Madison (Fields et al., 2022) frequently recognized caregiver roles in care organization, such as helping with tracking and scheduling appointments, taking notes before and during healthcare visits, and making lists of current medications.
I can concur. I took George to his appointments, acting as an administrative assistant and advocate. It was up to me to take notes, ask for what he needed, and verify or dispel inconsistent information (test results, guidance, data, etc.) between different doctors. I had a spreadsheet that the nurses loved, because it listed all the pertinent information about his medication names, amounts, prescribing doctor, reasons for taking them, etc.
Patient Advocacy
Advocacy is about empowering individuals to obtain resources. In the same Wisconsin study, several participants described experiences where the caregiver advocated on behalf of the patient when experiencing serious health complications linked to diabetes.
I was no different. As the months went on, George’s depression intensified into hopelessness and an “I don’t care anymore” attitude. So in addition to caregiving, I was also a fierce advocate for his mental health, trying to find resources to alleviate his chronic pain and help him feel more comfortable.
Financial Support
Financial support refers to help with planning and using financial resources. With rising home and institutional care costs and formal caregiver shortages, 66% of caregivers use their retirement and savings funds to pay for care (Genworth).

Applying for Social Security disability payments was a huge challenge. One of the questions that caused a denial related to his unemployment status. He explained that his medications made him fall asleep intermittently and randomly, so he couldn’t work. They blamed his medication and denied his application two more times before he was finally approved. He then started receiving payments of about $700 per month.
George had no life insurance, and I didn’t receive any direct financial support until his last week of life. I wrote Facebook posts about his status while he was in hospice care, and many of my friends sent funds via PayPal and Cashapp to help me pay for the funeral.
Navigating Healthcare Systems and Insurance Complexities

Caregiving at home often leads to substantial financial strain due to the cost of medical supplies, home health aides, and necessary modifications to the home. Not to mention the daunting task of navigating health insurance complexities, from finding in-network healthcare providers, care coordination, and working with billing offices regarding Medicare and Medicaid.
Finding In-Network Medical Providers
Another huge barrier for caregivers and patients alike is finding healthcare providers within their insurance network—especially specialists like those George needed. According to a Kaiser Family Foundation study, 29% of people struggle to find new providers within their network. Providers change the insurers they participate with frequently, and the onus is on the caregiver or patient to figure out how much of their bill will be covered in any given scenario.
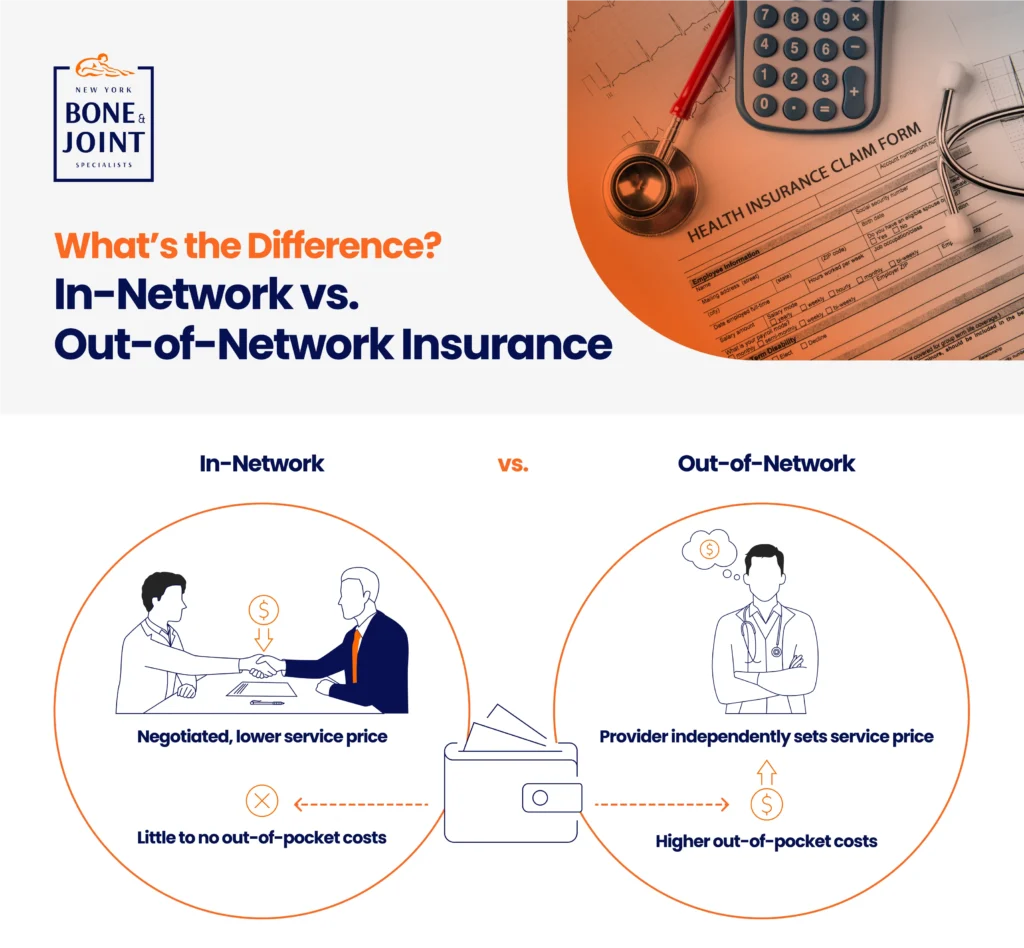
I’ve had to seek therapy before I met George, not just during his illness. No matter what, it’s difficult to find an available, local provider. Once I found a therapist, we started off going to see her together, but eventually he stopped.
Thomas recommends using online directories, insurance company tools and telehealth services to find these providers. And Dr. McAllister mentions an advanced step I’d never heard of before: “If you can’t find an in-network provider for your loved one, you can obtain a single case agreement, where your company will recognize the out-of-network provider as if they were in-network.”
Decoding the Difference Between Primary and Secondary Payer Insurance
One recurring source of frustration for me was dealing with multiple billing departments about George’s insurance. The health insurance from my employer was primary, and Medicare was secondary. I made this clear for each medical provider (remember, he had 10 doctors). However, each billing department would call me to confirm multiple times based on how his claims were processed.
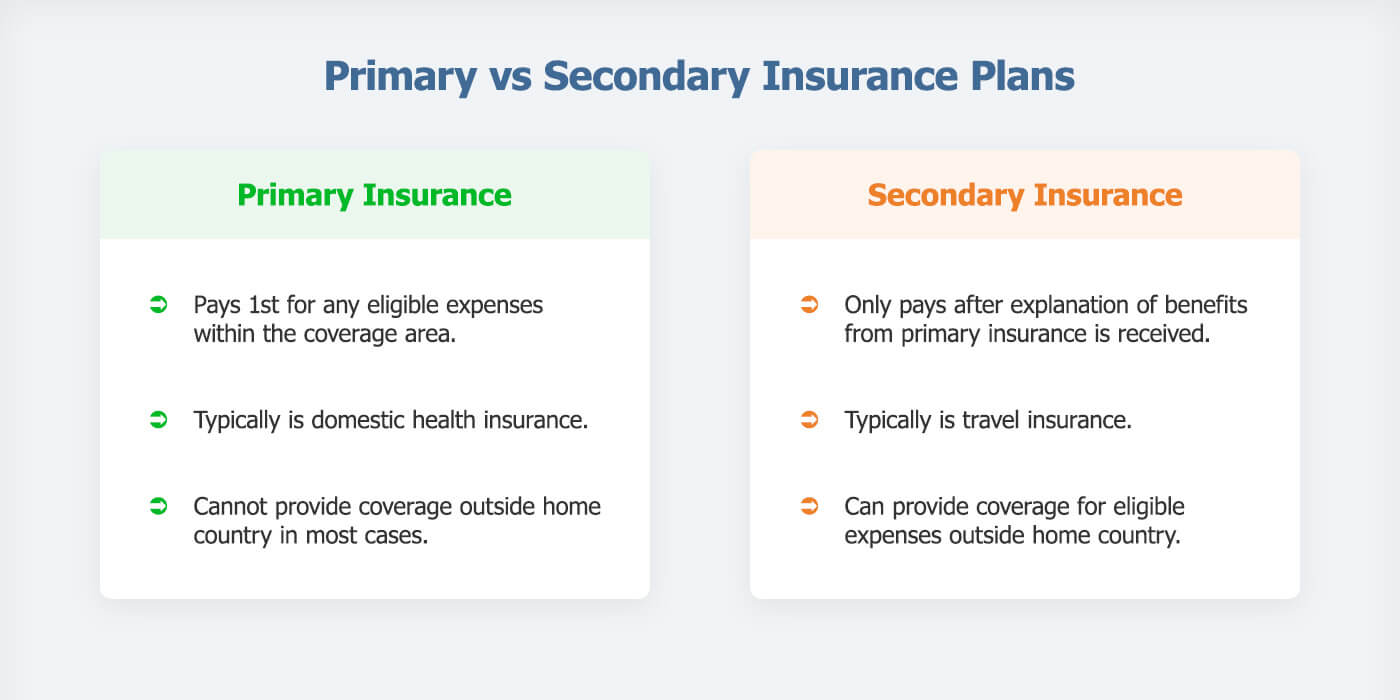
The coordination of benefits between private insurance and Medicare/Medicaid is something Shawn Plummer, CEO of The Annuity Expert educates his customers about. For example, he explains that determining the primary and secondary payers can help maximize coverage and minimize out-of-pocket expenses. Additionally, exploring supplemental insurance options can fill gaps not covered by primary insurance plans.
Healthcare providers have their struggles working with health insurance companies as well. Take for example Dr. McAllister’s practice, which is in-network with Medicare and out-of-network with all private insurance companies.
“As a provider, it’s so difficult to deal with insurance, although Medicare is very straightforward and easy to work with if you abide by their rules,” she says. “If you understand that private insurance companies try to maximize profit by denying coverage, and go into the process knowing how to advocate, you won’t feel as frustrated.
“To add to the confusion, when people have Managed Medicare, the medicare rules apply but the private insurance manages Medicare. “I often suggest sticking to straight Medicare, not Managed Medicare, because standard Medicare tends to treat providers more fairly. Many providers won’t accept Managed Medicare because of the low reimbursement rates and bureaucracy associated with private insurance companies.”
Bert Hofhuis of Sovereign Boss in the UK says that many insurance plans, including Medicare and private insurance, have limitations on what they cover for in-home care. “For example, Medicare may cover some home health services but often does not cover custodial care.”
Dr. McAllister, Hofhuis, and Plummer shared more tips to navigate complex insurance issues:

- Understand the specifics of health insurance policies: Ask questions about things you don’t understand, and “seek plans that cover in-home care services, medical supplies, and home modifications to be prepared,” says Hofhuis. “It’s essential to review policy details and consider supplemental insurance to cover gaps.”
- Take notes: “When dealing with insurance representatives on the phone, always write down the name of the person you speak with, information regarding the call and a reference for the call. Write everything down and email as much as possible so you have proof of everything,” Dr. Allister says.
- Use HSAs and FSAs: When available, Plummer and Hofhuis recommend usingHSAs and Flexible Savings Accounts (FSAs), which can provide tax-advantaged funds that can be used for medical expenses, including caregiving costs.
- Plan for long-term care: Consider purchasing long-term care insurance early to cover potential future caregiving needs.
- Keep records for tax purposes: Keep detailed records of caregiving expenses, as some may be tax-deductible, potentially easing your financial burden, Plummer and Hofhuis concur.
Denise M. Brown, is Founder and CEO of The Caregiving Years Training Academy, a family caregiving agency that coordinates care across multiple systems. She shares that Medicare Part B reimburses for Caregiver Training, Community Health Integration Services and Principal Navigation Services. Family caregivers can receive these services on behalf of a Medicare beneficiary if that beneficiary cannot participate in care planning because of their illness.
“The interplay between private insurance and Medicare/Medicaid is a common source of confusion,” Shah says. “More educational resources are desperately needed to help caregivers understand these complexities, including decision trees to determine primary and secondary payers.”
Effective Care Coordination Between Health Systems
Getting Access to Supplies and Services
The healthcare system is disconnected and siloed. The complications that come with coordinating care getting medical supplies can be a hassle for caregivers. It requires time, energy, patience and diligence. I remember having to take note of each and every resource to get various supplies, whether it was for dialysis, a wheelchair, or even gauze strips.
According to AARP, nearly 75% of caregivers manage medications and medical tasks. Thomas’ reader Sarah went through a nightmare trying to get the right wheelchair for her husband. “We had to go through so much paperwork and phone calls with the insurance company,” she said.
Shah understands these frustrations. “Partnerships between tech and medical supply companies to streamline this process for caregivers would be super helpful,” he says.
Brown was also a caregiver, and shares her perspective as a provider: “We do our scheduling based on the provider’s schedule, which means working around our own work schedule. We may need to be with our patients when the nurse or home health aide comes. Because of staffing shortages, we often take the schedule that’s given even when the schedule completely derails our day.”
Improving Systems and Patient Satisfaction
Brown says that healthcare professionals can help caregivers and agencies alike by obtaining doctor orders and making effective referrals. “It’s frustrating to have to repeatedly call the doctor’s office to get an order for home health services and durable medical equipment,.” she says.

“It’s also important that the healthcare professionals know which providers have staff available. For instance, my dad received home health services with a visiting nurse. When I also asked for a home health aide, the nurse was upfront that there just wasn’t the staff available for home health aide to visit. We could work around that because my sister and I provided my dad’s personal care. Others may not have the luxury, so it’s important to know the reality of what we can expect.
Another thing to consider is the emotional effect on the patient when a provider or aide is no longer available.
For example, there was a week when neither Brown nor her sister would be available on a Friday to care for their dad. “I was waiting to hear if my dad’s home health provider could continue providing services for my dad. I waited to reconfigure my work day on Friday if I needed to provide care. I later heard back from the home health agency that benefits would continue. My dad was worried about benefits ending in part because he had formed a wonderful friendship with his nurse, and he loves her. But the system doesn’t take into account the emotional impact when services end. We miss the care, and we often also miss the care provider.”

Naama Stauber Breckler, Co-founder of Better Health, is trying to improve accessibility and convenience for people with chronic conditions and dependent on different medical devices and supplies. “Patients need the ability to easily discover and order medical supplies online and get an easy explanation of their insurance benefits, how to maximize them, and how to find the best products,” she says.
Dr. McAllister recommends contacting the insurance company to see what exactly is allowed (HHA, PT, OT, SLP and RN services). “Companies may try to give you less than your family needs, but your insurance company will help you understand what your rights are. Many home health companies are short-staffed, but if you know what you can get for your family member, you will be able to advocate for the best,” she says.
Addressing Caregiver Challenges with Care at Home
Some of the ways to address in-home caregiver challenges include care-at-home and Hospital-at Home programs, using RPM, employer-provided benefits and flexible work arrangements, and better health plan coverage.
The Rise of Hospital-at-Home Programs
Care-at-home programs are integrated clinical programs created to deliver healthcare services that have either been traditionally provided within healthcare facilities or represent new care models for chronic disease management.
These programs typically combine remote insight into biometric data or symptoms via connected devices for remote patient monitoring (RPM) and communication with clinicians through telehealth modalities. Many care-at-home programs include
in-home services such as durable medical equipment (DME), meal delivery, technical support, and therapeutics.
66% of hospitals and health systems currently offer patients a care-at-home service. Early care-at-home programs were primarily targeted at ad hoc or episodic care, often only relying on a telehealth visit. But the growing maturity of these models and the confidence of the clinical and operational leaders make it increasingly viable to treat chronically and acutely ill patients at home. The differences between these program types include the amount and type of RPM, the in-home services included, and the staffing required to operate the program.
Providing remote care at home can reduce the need for hospital admissions/early discharge, freeing up valuable hospital resources and beds and leaving patients and their families feeling supported in their own homes.
Remote Monitoring for Patients with Chronic Conditions

George’s endocrinologist recommended that he use a Dexcom device to track his blood sugar. This remote monitoring device was great for me because no matter where I was or what time it was, the Dexcom app sent my phone a notification whenever his sugar was too high or too low. It was especially helpful when I attended a conference 6 hours from home, but got his alerts throughout the day and night. His family stayed with him when I was gone, but I got the alerts.
“Remote monitoring technologies have been game-changers for caregivers managing chronic conditions,” Shah says. “… allowing caregivers and clinicians to monitor vital signs and symptoms remotely, providing peace of mind and enabling more proactive care.”
The Current Health platform helps hospitals and clinics provide healthcare services to patients in their homes. Patients can use this platform for various health conditions, including COVID-19, heart problems, pregnancy care, and cancer.
Current Health conducted a survey in 2024 that shows caregiver interest in using health technology for their loved ones:
- Fall detection systems – 80%
- Voice-controlled assistive technology – 77%
- Telehealth apps – 70%
- Smart monitors – 70%
Survey respondents were confident that remote monitoring helps clinicians better understand the patient’s daily health.

Technology is essential to care-at-home programs, but the industry must embrace technology for these programs to be successful. According to another survey by Current Health and Sage Growth Partners, 51% of health system leaders cited patient engagement and adherence as a top challenge, with the most critical support service needs of clinical monitoring (54%), logistics (53%), and technical support (48%). In addition, interoperability between your care-at-home platform and the patient’s employee health record (EHR) is critical for reducing duplicative work for providers and ensuring you have a holistic view of the patient during and after their care-at-home experience.
RPM makes healthcare more accessible, as patients are monitored in their homes. Facing challenges such as high care costs, reduced revenue, and limited capacity, care at home is a cost-effective site of care that can provide better patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Employer Support
Employers can help by providing flexible work arrangements, paid leave, and Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) that offer counseling, legal help, financial advice, and referrals to eldercare services.

In-home caregiving can significantly impact an employee’s ability to manage their work responsibilities. Logan Mallory, VP of Marketing at Motivosity offers flexible work arrangements, like reduced or flexible work hours, to help alleviate the stress of balancing caregiving and work duties. This flexibility allows employees to be present for their loved ones while still fulfilling their work commitments.
Motivosity also offers their employees unlimited paid time off (PTO), health savings accounts (HSAs), and comprehensive health insurance to support our caregiving employees, each of which benefits the employees who are also caregivers in specific ways:
- Unlimited PTO ensures that employees can take the necessary time off without worrying about exhausting their leave.
- HSAs help cover the costs of medical supplies and services, providing financial relief.
- Health insurance plans that cover a wide range of services, including in-home care, which helps employees manage caregiving expenses more effectively. They also provide access to counseling services, stress management resources, mental health apps and gym access.
“While we can only do so much, employers should strive to provide as much support as possible to caregiving employees,” Mallory says. “By offering flexible solutions and understanding their unique challenges, we can help them manage their responsibilities more effectively.”
Health Plan Changes Needed
Insurance Coverage Gaps
In the U.S., patients and their caregivers could benefit from closing the following health insurance coverage gaps in their health plans:
- Long-Term Services and Supports (LTSS): According to the HHS, 70% of people over 65 will require some type of LTSS, which is not covered under Medicare or most private health insurance plans.
- Home and Community-Based Services (HCBS): There’s currently limited coverage for services that help with ADLs and care at home.
- Caregiver Support Services: Lack of comprehensive coverage for services that directly support family caregivers, such as respite care, training, and counseling in some states.
- Non-Expansion States: In states that have not expanded Medicaid, many low-income adults fall into a coverage gap, being ineligible for both Medicaid and Marketplace subsidies (Drake, et al., 2024).
- Insufficient Coverage for Working Caregivers: Many caregivers struggle to maintain full-time employment and may lose employer-sponsored health insurance (Tingey et al., 2020).
10 Ways Health Plan Changes Can Support Caregivers
- Expand Medicaid Coverage: Adopting Medicaid expansion in all states could provide coverage to approximately 2.9 million uninsured adults, including many caregivers (Drake et al., 2024).
- Integrate Caregiver Support: Incorporate caregiver support services into existing health care delivery models and value-based care programs.
- Implement Paid Family Caregiving Models: Develop programs that compensate family caregivers for their services, similar to Colorado’s program.
- Enhance LTSS and HCBS Coverage: Expand coverage for these services under Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurance plans to reduce out-of-pocket costs for families.
- Improve Remote Care Options: Expand coverage and availability of remote patient monitoring and telehealth services to support both patients and caregivers. Hospital-at-Home programs should be a mainstay in health plan coverage. These programs are customer-centric, result in lower hospital readmission rates, increase hospital capacity, and reduce issues with resource allocation among clinical staff.
- Develop Caregiver-Specific Insurance Products: Create insurance plans or supplemental coverage options designed to meet the unique needs of caregivers.
- Enhance Workplace Policies: Encourage employers to offer flexible work arrangements and maintain health insurance coverage for employees who are caregivers (Tingey et al., 2020).
- Improve Caregiver Identification and Assessment: Implement systematic processes in healthcare settings to identify, assess, and support caregivers.
- 9. Include Caregiver Metrics in Quality Measures: Incorporate caregiver experiences and outcomes into healthcare quality measurements to incentivize better support.
- Prepare Healthcare Professionals: Enhance training for healthcare providers on person- and family-centered care to better support caregivers. Psychoeducational information (e.g., treatment, lifestyle, etc.) and healthcare (e.g., emotional support, practical services, etc.) were the most common unmet need domains across health conditions (Thomas et al, 2023). Addressing unmet informational or healthcare needs may help optimize outcomes and care for children and families living with common chronic health conditions.
By addressing these gaps and implementing these improvements, the U.S. healthcare system could significantly enhance support for both caregivers and patients by reducing the financial and emotional burden on families while improving overall care outcomes.
Supporting Caregivers and Their Families

As we’ve explored throughout this article, home care programs and RPM offer transformative benefits for both patients and caregivers. These solutions provide enhanced flexibility, improved care coordination, crucial support for managing chronic conditions and reducing caregiver burden. Expanding health plan coverage for these programs is not just beneficial, but necessary.
Hospital-at-Home (HaH) programs, in particular, represent a cost-effective, patient-centered approach that deserves widespread adoption. Every health institution could likely benefit from such a program to increase the capacity of their facility, enhance customer-centricity and patient satisfaction, and promote better patient outcomes. It’s the way of the future, and the way patients want to receive care. So we call on healthcare providers and health plans to prioritize the inclusion of care-at-home programs in their coverage.
By supporting caregivers and improving patient outcomes, we can create a more efficient, compassionate healthcare system. This requires a collaborative effort from healthcare providers, insurers, policymakers, and technology innovators to truly enhance the caregiving experience and, ultimately, the quality of life for both patients and their dedicated caregivers.
References
Carter, K., Blakely, C., Zuk, J., Brittan, M., & Foster,C. Employing Family Caregivers: An Innovative Health Care Model. Pediatrics. 2022; 149(6), 1-4. doi.org/10.1542/peds.2021-054273
“Compensation For Caregiving.” Colorado Respite Coalition, https://coloradorespitecoalition.org/family-caregivers/compensation-for-caregiving.php. Accessed 2 July 2024.
Costa, S., Ferreira, J., Leite, Â., & Pereira, M. G. (2021). Traumatic stress as a mediator of quality of life and burden in informal caregivers of amputees due to diabetic foot: a longitudinal study. Health Psychology Report, 9(4), 339, 345. https://doi.org/10.5114/hpr.2020.101495
Drake, P., Tolbert, J., Rudowitz, R, & Damico, A. “How Many Uninsured Are in the Coverage Gap and How Many Could be Eligible if All States Adopted the Medicaid Expansion?” KFF, 26 Feb. 2024, https://www.kff.org/medicaid/issue-brief/how-many-uninsured-are-in-the-coverage-gap-and-how-many-could-be-eligible-if-all-states-adopted-the-medicaid-expansion. Accessed 2 July 2024.
Fakeye, M.B.K., Samuel, L.J., Drabo, E.F., Bandeen-Roche, K., & Wolff, J.L. Caregiving-Related Work Productivity Loss Among Employed Family and Other Unpaid Caregivers of Older Adults. Value in Health. 2023;26(5):712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2022.06.014
Favreault, M., Dey, J., Anderson, L., Lamont, H., & Marton, W. “Future Change in Caregiving Networks: How Family Caregivers and Direct Care Workers Support Older Adults Now and in the Future.” Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation, 2 Aug, 2023, https://aspe.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/documents/a449863a8c93838d37f78ccf29e9231f/future-change-caregiving-networks.pdf. Accessed 2 July 2024.
Fields B., Makaroun L., Rodriguez K.L., Robinson C., Forman J., & Rosland A-M. Caregiver role development in chronic disease: A qualitative study of informal caregiving for veterans with diabetes. Chronic Illness. 2022;18(1):193, 196. doi:10.1177/1742395320949633
“How Caregiving Impacts Families, Communities and Society.” Genworth, 27 Oct. 2021, https://pro.genworth.com/riiproweb/productinfo/pdf/682801BRO.pdf. Accessed 2 July 2024.
Ibrahim N., Chu S., Siau C., Amit N., Ismail R., Halim A., & Gafor, A. The effects of psychosocial and economic factors on the quality of life of patients with end-stage renal disease and their caregivers in Klang Valley, Malaysia: protocol for a mixed-methods study. BMJ Open. 2022;12(6):1-2. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-059305
Katsarou, A., Intas, G., & Pierrakos, G. Investigating the Needs of Caregivers of Patients Suffering from Chronic Diseases: A Mixed-Method Study. Indian Journal of Palliative Care. 2023; 29(3), 285-286. https://doi.org/10.25259/IJPC_179_2022
Khurana, Sanjay. “Caregiver Support | Gaps, Opportunities and Emerging Models in Healthcare.” Linkedin, 19 Oct. 2023, https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/caregiver-support-gaps-opportunities-emerging-models-sanjay-khurana. Accessed 2 July 2024.
Smith, Morgan. “90% of companies say they’ll return to the office by the end of 2024—but the 5-day commute is ‘dead,’ experts say.” CNBC, 11 Sept. 2023, https://www.cnbc.com/2023/09/11/90percent-of-companies-say-theyll-return-to-the-office-by-the-end-of-2024.html. Accessed 26 June 2024.
Thomas S., Ryan N.P., Byrne L.K., Hendrieckx C., White V. Unmet supportive care needs of families of children with chronic illness: A systematic review. Journal of Clinical Nursing. 2023; 32(19-20): 7101. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.16806
Tingey, J.L., Lum, J. Morean, W., Franklin, R., & Bentley, J.A. Healthcare Coverage and Utilization Among Caregivers in the United States: Findings From the 2015 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. Rehabilitation Psychology. 2020; 65(1), 63-71. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/rep0000307
Umrigar D, Mhaske R. Psychological Health of Wives’ of Patients with Chronic Illnesses. Journal of Psychological Research. 2022;4(1):1-2. doi:10.30564/jpr.v4i1.3879









































