In an era where digital healthcare is becoming increasingly prevalent, Amwell is a prominent player in the telehealth arena. But how does Amwell stack up against its competitors?
This in-depth Amwell telehealth review will explore the ins and outs of Amwell’s telehealth services, to help you decide if it’s the right choice for your healthcare needs.
Contents
What is Amwell and How Does It Work?
Amwell is a leading telehealth platform that connects patients with healthcare providers digitally.
You can access their services from virtually anywhere with internet access or their mobile app. From urgent care to behavioral health, Amwell’s platform is designed to cater to various healthcare needs.
Available medical services
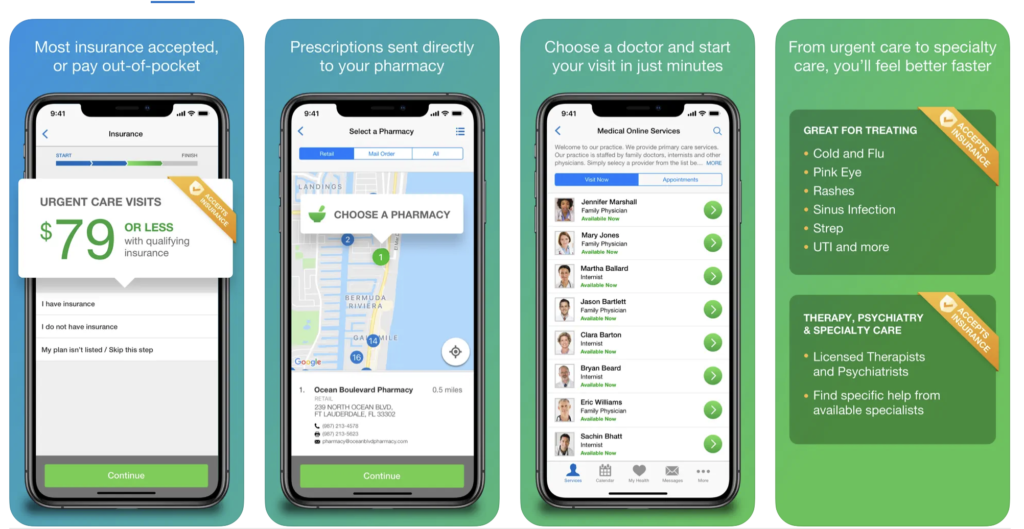
Amwell offers a broad spectrum of medical services, including:
- Primary Care: General health consultations.
- Urgent Care: Immediate care for non-emergency conditions.
- Behavioral Health: Therapy and counseling services.
- Specialist Appointments: Access to dermatologists, dietitians, and more.
- Prescriptions: Medication management and prescription refills.
How to schedule and start a virtual doctor visit
Scheduling an appointment with Amwell is straightforward:
- Enroll: Create an account on the Amwell platform.
- Choose: Select a doctor based on their experience and ratings.
- Visit: Start your video call using secure, high-quality streaming video.
Most doctor visits last about 10 minutes, but you can extend the time if needed. These doctors can review your medical history, diagnose conditions, and prescribe medications if necessary.
Technical requirements

To use Amwell, you need:
- A computer or mobile device.
- A stable internet connection.
- The Amwell app or access to the web-based platform.
If you’re unable to use video, you can call for an audio-only (phone) visit as well. However, you may not be able to obtain a new prescription with an audio-only visit, depending on the state where you live.
Amwell’s Features and Benefits
Next, let’s review Amwell’s valuable features and benefits.
24/7 availability for urgent care
One of the standout features of Amwell is its 24/7 availability. You can access urgent care services anytime, even in the middle of the night or on a holiday.
Range of specialists available

You can choose from a variety of specialists at Amwell, including therapists, neurologists, dermatologists, and dietitians. This broad range of services ensures that you can find the right expert for your specific healthcare needs.
Some examples of conditions Amwell’s urgent care doctors treat include:
- Acute Bronchitis
- Headache
- Fever & Flu
- Back pain
- UTI
- Respiratory Infection
- Sprains and strains
- Diarrhea
- Exacerbations of chronic disease (asthma, diabetes)
103,000 providers conducted visits via Amwell in 2023.
Prescription services and management
Amwell doctors can prescribe medications and send them directly to your preferred pharmacy. This is particularly helpful to manage ongoing treatments and chronic conditions, and get your necessary medications fast.
Note: A video visit is required by most states (not an audio-only visit) before Amwell can prescribe medication.
Integration with health insurance plans
Amwell works with several health insurance providers, making it easier for patients to get covered services. They also offer options for uninsured patients. Let’s dig into that a bit more, shall we?
Cost and Insurance Coverage
Understanding costs and insurance coverage is crucial when considering a telehealth service. This section discusses Amwell’s pricing.

Amwell pricing
The costs you pay for Amwell visits vary by visit type and insurance coverage:
- Urgent Care: The cost starts at $69, unless your insurance co-pay is lower.
- Mental Health: Therapy sessions range from $99 to $110, depending on the therapist’s qualifications.
- Psychiatry: The initial visit for a psychiatric consultation is more expensive at $279. Follow-up visits with the same provider are $109 per visit.
Amwell works with many insurance companies, which can lower your costs. Before booking an appointment, check with your insurance provider. If you don’t have insurance, Amwell still offers competitive pricing.
Comparison with traditional in-person visits
Telehealth visits on Amwell are often more affordable than traditional in-person visits. The convenience of not having to travel and the ability to access care at any time makes it even more cost-effective.
Insurance plans accepted by Amwell
Amwell partners with various insurance companies, including Aetna, Blue Cross Blue Shield, UnitedHealthcare, and Anthem. Many insurance plans cover urgent care and mental health (behavioral health) services to reduce out-of-pocket costs.
Over 100 million members have Amwell as a covered benefit. To confirm insurance coverage and pricing, check with your insurance provider before making an appointment.
For those without insurance, Amwell offers competitive pricing for its services. The platform ensures that everyone can access quality healthcare, regardless of their insurance status.
A user-friendly platform is essential for effective telehealth services. Let’s examine Amwell’s interface next.
User Experience and Interface
An easy-to-use interface* is essential for a telehealth platform, and Amwell fits the bill.

Easy account creation and setup
Creating an account on Amwell is quick and straightforward. The platform guides you through the process, and securely stores your information for future visits.
Navigation of the Amwell app and website
Both the Amwell app and website are designed with user experience (UX) in mind. The intuitive layout makes it easy to find doctors, schedule appointments, and access medical records.
Quality of video consultations
Amwell uses high-quality streaming video for consultations, ensuring clear communication between patients and doctors. This feature is crucial for accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
Patient support and resources
Amwell offers robust patient support, including FAQs, live chat, and phone support. These resources help users navigate the platform and resolve any issues they may encounter.
Is it safe to use Amwell services over the internet? How does Amwell ensure patient data is protected? We answer these questions next.
Privacy and Security Measures
Privacy and security are paramount in telehealth services. Here’s how Amwell addresses privacy and security concerns.

HIPAA compliance and data protection
Amwell is fully compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), which ensures patient information is securely handled and protected.
Secure messaging and file sharing
The platform uses encrypted messaging and secure file-sharing protocols to protect patient data during communication and consultations.
Patient data storage and access policies
Amwell stores patient data securely, and you can access your medical records anytime. This transparency helps build trust and ensures you have control over your health information.
To provide a balanced view, let’s consider the advantages and potential drawbacks of using Amwell.
Pros and Cons of Using Amwell

Understanding patient feedback can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of a telehealth service. And like any service, Amwell has its advantages and potential drawbacks.
Amwell has mixed reviews from users. Amwell offers competitive pricing and a wide range of services compared to other telehealth providers.
While many praise the convenience and quality of care, others expressed dissatisfaction with customer service, appointment scheduling, and reliability.
Here’s what people who’ve used Amwell had to say about their experience.
Amwell’s advantages
Amwell’s platform includes all the benefits of a telehealth platform:
- Convenience: Access healthcare from anywhere at any time from a user-friendly interface.
- Range of Services: From urgent care to specialist consultations.
- Cost-Effective: Often cheaper than in-person visits.
- Insurance Integration: Works with many insurance providers.
J.D. Power has recognized Amwell for its high customer satisfaction for several years. Amwell ranked No. 1 in the J.D. Power 2020 U.S. Telehealth Satisfaction Study, and only dropped to third place in 2023 behind CVS (1st) and MDLive (2nd).
Potential drawbacks
Based on reviews from those who’ve used Amwell, there are a few issues you may encounter, such as:
- Technical Issues: Some users report difficulties with video quality and connectivity.
- Customer Service: There are complaints about slow response times and unresolved billing issues.
- Appointment Availability: Some people had long wait times and appointment cancellations.
Conclusion

Amwell’s telehealth platform provides convenient, accessible, and cost-effective healthcare services. With its wide range of services, 24/7 availability, and integration with many insurance plans, it’s a solid option for those seeking virtual healthcare. However, like any telehealth service, there are areas for improvement.
Whether you’re looking for urgent care, specialist consultations, or mental health services, Amwell provides a comprehensive solution that could meet your various healthcare needs. Consider your specific healthcare needs, the types of services you require, and your comfort level with virtual consultations when deciding if Amwell is right for you.
* I offer UX copywriting and content design services.
References
Amwell. (n.d.). Trustpilot. Retrieved from https://www.trustpilot.com/review/amwell.com
Amwell for patients: How it works. (n.d.). Amwell. Retrieved from https://patients.amwell.com/how-it-works
Amwell for patients: Online doctor visits, 24/7. (n.d.). Amwell. Retrieved from https://patients.amwell.com
Amwell Ranked No. 1 in the J.D. Power 2020 U.S. Telehealth Satisfaction Survey. (2020). Amwell. Retrieved from
Enabling hybrid care at scale. (n.d.). Amwell. Retrieved from https://business.amwell.com/
Mixed reviews for Amwell: Long Wait Times, Appointment Cancellations, and Billing Concerns. (n.d.). Kimola. Retrieved from https://kimola.com/reports/unlock-insights-with-amwell-customer-feedback-analysis-trustpilot-en-us-148604
Telehealth Mobile Apps: Preferred Channel for Virtual Care Delivery but Generational Difference Persits, J.D. Power Finds. (2023). J.D. Power. Retrieved from https://japan.jdpower.com/en/press-releases/2023_US_Telehealth_Satisfaction_Study








































