Sundown syndrome, or “sundowning,” affects many elderly individuals, particularly those with dementia or Alzheimer’s disease. This challenging condition causes behavioral changes as daylight fades into evening. Up to 20% of people with Alzheimer’s experience sundowning symptoms. For family caregivers, managing sundown syndrome every day can be exhausting. Let’s look at some practical, evidence-based approaches to recognize, minimize and manage the effects of sundown syndrome.
Contents
- What is Sundown Syndrome?
- Practical Management Strategies
- Medical Interventions and Therapies for Sundowning Symptoms
- Caregiver Support
What is Sundown Syndrome?

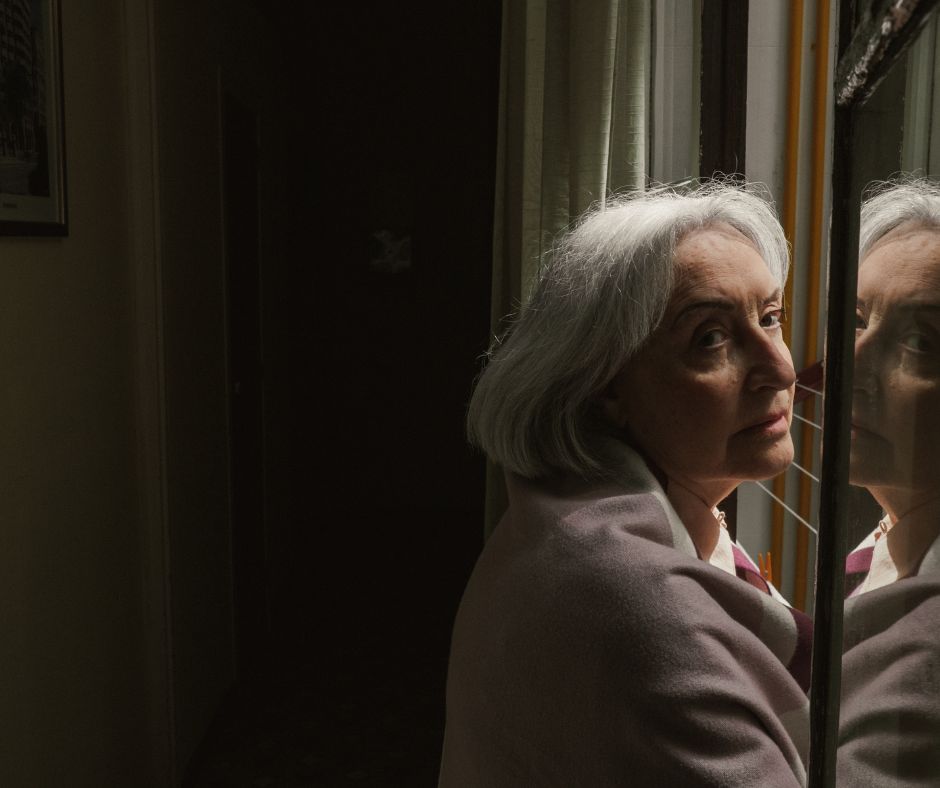
Sundown syndrome, also known as sundowning, is a set of neuropsychiatric symptoms such as confusion, anxiety, agitation, pacing, and wandering that intensify as daylight fades. These behaviors can persist well into the night, disrupting sleep patterns and causing distress.
The exact causes of sundowning are not fully understood, but several factors play a role:
- Disruptions in circadian rhythm
- Fatigue and exhaustion from daily activities
- Changes in lighting and increased shadows
- Hormonal imbalances such as decreased melatonin production
Sundowning primarily affects individuals with dementia, particularly those with Alzheimer’s disease. However, it can also occur in elderly people without dementia, especially those in care facilities or hospitals.
The biological causes of sundowning behaviors are complex. Research shows these causes may be damage to the brain’s cholinergic system and hormonal disruptions (such as problems with the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis) that helps control stress and bodily functions. Additionally, reduced melatonin production in aging people can further disrupt normal sleep-wake cycles.
Recognize the early warning signs

Identifying the early signs of a sundowning episode can help you as a caregiver to intervene quickly and potentially prevent or minimize symptoms. Some behaviors to watch for are:
- Increased restlessness or agitation as the day progresses
- Mood changes, such as becoming more anxious or suspicious
- Difficulty concentrating on tasks
- Pacing or wandering more frequently
- Shadowing caregivers or becoming more clingy

It’s essential to distinguish sundowning from other health issues. Unlike conditions such as delirium, sundowning symptoms typically follow a predictable pattern, worsening in the late afternoon or evening and often improving by morning.
Tracking patterns and triggers can be invaluable for managing sundowning. Keep a simple log noting:
- Time of day symptoms appear
- Duration of episodes
- Potential triggers (noise, visitors, certain activities, and foods)
- Effectiveness of interventions
This information can help identify patterns and develop targeted strategies to minimize symptoms.
Practical Management Strategies
When sundowning symptoms occur, having a toolkit to reduce symptoms can help you respond effectively and with compassion. Here are some practical approaches.

Distraction and redirection techniques
To help redirect and calm your loved one:
- Engage the person in a favorite activity or hobby
- Use calming objects like stress balls or fidget toys
- Redirect attention to pleasant memories or topics of interest
Calming communication approaches
Your tone of voice influences how people with Alzheimer’s respond and react, so be sure to:
- Speak in a soft, reassuring tone
- Use simple, clear language
- Avoid arguing or correcting; instead, validate feelings and redirect
Gentle exercise options

Walking has been shown to reduce the symptoms of sundowning and improve sleep quality. Some ways to engage in gentle exercise with a person exhibiting sundowning include:
- Take a short walk together (if safe and appropriate)
- Practice seated exercises or stretches
- Engage in simple dance movements to calming music
Crisis management for severe episodes
- Ensure the environment is safe and remove potential hazards
- Use calming techniques like deep breathing or gentle touch
- If necessary, contact healthcare providers for additional support
Remember, the effectiveness of these strategies may vary. Be patient and willing to try different approaches to find what works best for your loved one.
Create a soothing environment
Environmental factors play a significant role in relieving sundowning behaviors or making them worse. Making thoughtful adjustments to the living space can create a calming atmosphere that may reduce symptoms.
Optimal lighting arrangements

- Increase indoor lighting in the late afternoon to minimize shadows
- Use nightlights to reduce confusion during nighttime wakings
- Consider light therapy boxes to help regulate circadian rhythms
Noise management
- Reduce background noise from TVs or radios in the evening
- Use white noise machines or soft music to create a soothing ambiance
- Encourage quiet activities as bedtime approaches
Temperature and comfort

Sundown syndrome is linked to changes in body temperature and activity patterns. People with this condition often have:
- Less daytime activity
- More nighttime activity
- Later peak activity times
- Higher average body temperature
- Later peak temperature times
These changes can make their daily rhythms more irregular. To mitigate this, you should:
- Maintain a comfortable room temperature, typically between 68°F to 72°F (or 20°C to 22°C)
- Ensure bedding and clothing are appropriate for your loved one’s environment
- Address any physical discomfort that might contribute to agitation
Familiar and consistent setting
- Keep frequently used items in consistent locations
- Display familiar objects and photos to create a sense of security
- Minimize changes to the environment when possible
Organize the physical space
- Remove clutter to reduce confusion and potential hazards
- Use clear labels or signs to help with navigation
- Consider safety measures like door alarms or motion sensors for wandering prevention
Use these environmental strategies to create a more supportive and calming atmosphere for people experiencing sundowning.
Establish effective daily routines

Consistent daily schedules can significantly reduce sundowning symptoms by providing structure and predictability.
Set a consistent schedule
As a caregiver, you should aim to:
- Wake up and go to bed at the same time each day
- Plan meals and snacks at regular intervals
- Schedule important appointments or activities earlier in the day when alertness is typically higher
Plan meaningful activities

- Engage in stimulating activities in the morning and early afternoon
- Involve the person with Alzheimers in simple household tasks they enjoy
- Encourage reminiscing with photo albums or familiar objects
- Gradually transition to calmer activities as the day progresses
- Avoid overstimulating events or outings in the late afternoon or evening
- Engage in gentle, repetitive activities in the evening like folding laundry or sorting items
Meal timing and dietary considerations
- Keep the table setting and meal simple
- Serve the main meal earlier in the day and allow plenty of time to eat
- Limit caffeine and sugar intake (especially after lunch)
- Offer a light snack before bedtime to prevent hunger-related agitation
Sleep hygiene practices

- Create a relaxing bedtime routine (warm bath, gentle stretching)
- Ensure the bedroom is dark, quiet, and at a comfortable temperature
- Limit screen time and exposure to blue light in the evening
Here’s a sample daily schedule to minimize sundowning triggers:
- 7:00 AM: Wake up, morning hygiene routine
- 8:00 AM: Breakfast and medications
- 9:00 AM – 12:00 PM: Engaging activities (puzzles, crafts, gentle exercise)
- 12:30 PM: Lunch
- 1:30 PM – 3:30 PM: Quiet time or short nap
- 3:30 PM – 5:00 PM: Light activities, increase indoor lighting
- 5:30 PM: Light dinner
- 6:30 PM – 8:00 PM: Relaxing activities (soft music, gentle massage, or a short walk)
- 8:30 PM: Begin bedtime routine
- 9:30 PM: Lights out
Remember to remain flexible. Adjust the schedule as needed based on individual preferences and symptoms.
Medical Interventions and Therapies for Sundowning Symptoms
Interventions without medicine are typically the first line of treatment for sundowning, but medication is necessary in some cases. Always consult with healthcare providers before starting a new medicine.

Medication options
Some of the medicines healthcare providers use to treat the symptoms of sundowning are:
- Low-dose antipsychotics
- Melatonin supplements to regulate sleep-wake cycles
- Cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s-related sundowning
Non-pharmaceutical approaches

- Light therapy: Exposure to bright light during the day may help regulate circadian rhythms
- Music therapy: Listening to familiar, calming music can reduce anxiety and agitation
- Aromatherapy: Certain scents like lavender may promote relaxation
Supplements and natural remedies
- Herbal teas (chamomile, valerian root)
- Essential oils for aromatherapy
- Magnesium supplements (under medical supervision)
Discuss any supplements or natural remedies with a healthcare provider to ensure safety and avoid potential interactions with medications.
Addressing underlying health issues
Treating underlying conditions that may contribute to sundowning is crucial. These may include:
- Pain or discomfort
- Urinary tract infections
- Sleep apnea
- Depression or anxiety
When to consult a healthcare provider
Contact your loved one’s healthcare provider if:
- Their symptoms significantly impact quality of life or safety
- Non-pharmacological approaches have been ineffective
- You have concerns about their underlying health issues
Be sure your loved one gets regular health check-ups, and have open communication with healthcare providers to help identify and address these issues promptly.
Caregiver Support

Caring for someone with sundown syndrome can be physically and emotionally demanding. Recognizing the importance of caregiver well-being is essential for sustainable, quality care.
Caregiver burnout warning signs
- Feeling constantly exhausted or overwhelmed
- Neglecting personal health or relationships
- Experiencing mood swings or irritability
- Losing interest in previously enjoyed activities
Learn how to prevent burnout before it affects your caregiving.
Respite care options
Explore respite options such as:
- Adult day care centers
- In-home respite services
- Short-term residential care facilities
A study in the The Gerontologistfound that regular use of respite care services can often reduce caregiver stressand improve overall well-being.

Building a support network
You’re not alone in this journey. Connecting with other caregivers can help you de-stress and learn strategies to maintain your energy and mental health:
- Join local support groups for caregivers
- Enlist help from family members and friends
- Consider hiring part-time professional caregivers
Self-care strategies
- Practice stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga
- Maintain a healthy diet and exercise routine
- Set aside time for hobbies and personal interests
- Seek professional counseling if needed
Resources for caregiver education and support
- Alzheimer’s Association (www.alz.org)
- National Institute on Aging (www.nia.nih.gov)
- Local senior centers and community organizations
Managing sundown syndrome requires patience, consistency, and compassionate understanding. Each person’s experience is unique, so finding the right combination of strategies may take time. With the right approach, people experiencing sundown syndrome and their caregivers can enjoy more peaceful evenings and improved quality of life.
References
7 Tips for Coping with Sundowner’s Syndrome. (n.d.). Banner Health. Retrieved from https://www.bannerhealth.com/healthcareblog/better-me/7-tips-for-coping-with-sundowners-syndrome
Antipsychotics and other drug approaches in dementia care. (2021). Alzheimer’s Society. Retrieved from https://www.alzheimers.org.uk/about-dementia/treatments/dementia-medication/antipsychotic-drugs
Canevelli, M., Valletta, M., Trebbastoni, A., Sarli, G., Tariciotti, L., & Bruno, G. (2016). Sundowning in Dementia: Clinical Relevance, Pathophysiological Determinants, and Therapeutic Approaches. Frontiers in Medicine, 3, 73. doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2016.00073
Cardinali, D. P., Furio, A. M., & Brusco, L. I. (2010). Clinical Aspects of Melatonin Intervention in Alzheimer’s Disease Progression. Current Neuropharmacology, 8(3), 218-227. doi.org/10.2174/1570159107922462096
Food and Eating. (n.d.). Alzheimer’s Association. Retrieved from https://www.alz.org/help-support/caregiving/daily-care/food-eating
Get More Out of Sundowner Distraction Techniques. (2021). Tracy Cram Perkins. Retrieved from https://tracycramperkins.com/get-more-out-of-sundowner-distraction-techniques/
Goyer, A. (2017). 11 Ways to Manage Sundown Syndrome. Retrieved from https://www.aarp.org/caregiving/health/info-2017/ways-to-manage-sundown-syndrome.html
Jacob, D. & Kahan, S. (n.d.). How Do Cholinesterase Inhibitors Work? RxList. Retrieved from https://www.rxlist.com/how_do_cholinesterase_inhibitors_work/drug-class.htm
Kernisan, L. (2025). 5 Types of Medication Used to Treat Sundowning & Difficult Dementia Behaviors. Better Health While Aging. Retrieved from https://betterhealthwhileaging.net/medications-to-treat-difficult-alzheimers-behaviors/
Khachiyants, N., Trinkle, D., Son, S. J., & Kim, K. Y. (2011). Sundown Syndrome in Persons with Dementia: An Update. Psychiatry Investigation, 8(4), 275. doi.org/10.4306/pi.2011.8.4.275
Sample Daily Schedule for Elderly: Create a Routine for Your Loved One. (n.d.). Global One Home Care. Retrieved from https://globalonehomecare.com/sample-daily-schedule-for-elderly/
Shih, Y.H., Pai, M.C., Huang, Y.C., & Wang, J.J. (2017). Sundown Syndrome, Sleep Quality, and Walking Among Community-Dwelling People With Alzheimer Disease. Journal of American Medical Directors Association (JAMDA), 18(5):396-401. doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2016.10.016
Sleep Issues and Sundowning. (n.d.). Alzheimer’s Association. Retrieved from https://www.alz.org/help-support/caregiving/stages-behaviors/sleep-issues-sundowning
Sundown Syndrome: Causes, Treatment, and Advice for Caregivers. (2024). Neural Effects. Retrieved from https://neuraleffects.com/blog/sundown-syndrome-causes-and-treatment-options/
Sundowners Syndrome: Triggers, Symptoms & Management. (n.d.). Keystone Health. Retrieved from https://keystone.health/sundowners-syndrome
Sundowning. (n.d.). Physiopedia. Retrieved from https://www.physio-pedia.com/Sundowning
Thomas, T. & Ritter, A. (2022). Wandering & Sundowning in Dementia. Practical Neurology. Retrieved from https://practicalneurology.com/articles/2022-june/wandering-sundowning-in-dementia
Watson, S., Goodman, B. & Mitchell, K. (2024). How to Effectively Manage Sundowning. WebMD. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/alzheimers/manage-sundowning
Ways Caregivers Can Support Seniors in Sundowing Care. (2025). Homewatch Caregivers. Retrieved from https://www.homewatchcaregivers.com/blog/chronic-conditions/4-ways-caregivers-can-support-seniors-in-sundown/
Zarit, S. H., Kim, K., Femia, E. E., Almeida, D. M., & Klein, L. C. (2014). The Effects of Adult Day Services on Family Caregivers’ Daily Stress, Affect, and Health: Outcomes From the Daily Stress and Health (DaSH) Study. The Gerontologist, 54(4), 570-579. doi.org/10.1093/geront/gnt045